算法分析
算法分析的目的是预测算法所需的资源,如计算时间(CPU 消耗)、内存空间(RAM 消耗)、通信时间(带宽消耗)等,以及预测算法的运行时间,即在给定输入规模时,所执行的基本操作数量,或者称为算法复杂度。
算法的运行时间取决于输入的数据特征,输入数据的规模和运行时间的上限(因为运行时间的上限是对使用者的承诺)。算法分析一般忽略掉那些依赖于机器的常量,而关注运行时间的增长趋势。一般仅考量算法在最坏情况下的运行情况,使用 O 记号法表示最坏运行情况的上界。例如:
线性复杂度O(n) 表示每个元素都要被处理一次。
平方复杂度 O(n2)表示每个元素都要被处理 n 次。
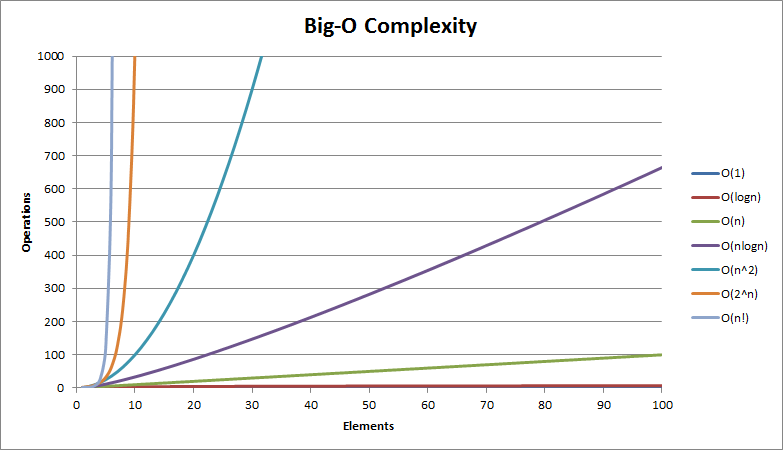
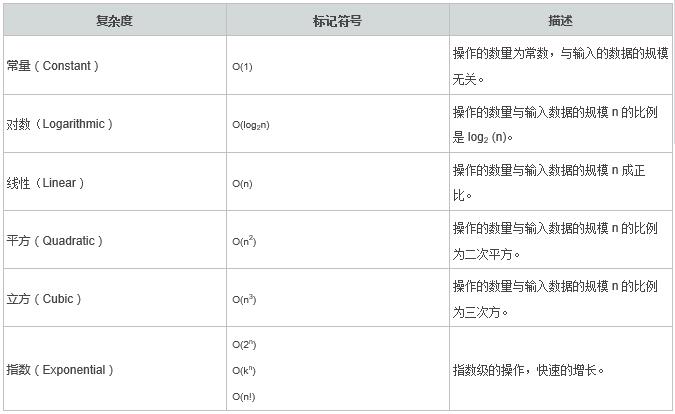 不同时间复杂度中元素数量与操作次数的关系图:
不同时间复杂度中元素数量与操作次数的关系图:
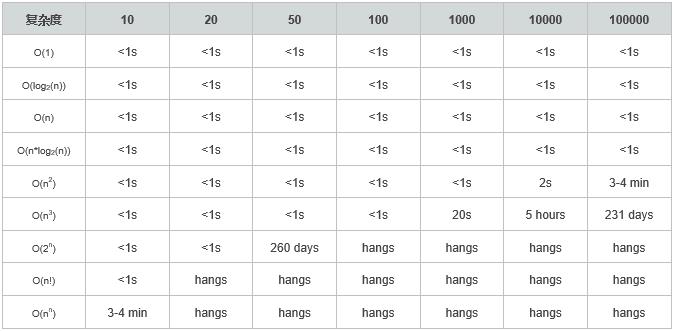
而通常时间复杂度与运行时间有一些常见的比例关系:
计算代码块的渐进运行时间,即算法复杂度的方法有如下步骤:
1、确定决定算法运行时间的组成步骤。
2、找到执行该步骤的代码,标记为 1。
3、查看标记为 1 的代码的下一行代码。如果下一行代码是一个循环,则将标记 1 修改为 1 倍于循环的次数 1 * n。如果包含多个嵌套的循环,则将继续计算倍数,例如 1 * n * m。
4、找到标记到的最大的值,就是运行时间的最大值,即算法复杂度描述的上界。
如,斐波那契数列:
Fib(0) = 0,Fib(1)= 1,Fib(n) = Fib(n-1) + Fib(n-2)
F() = 0, 1, 1, 2, 3,5, 8, 13, 21, 34 …
例1
int Fibonacci(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
else
return Fibonacci(n - 1) + Fibonacci(n -2);
}
这里,给定规模 n,计算Fib(n) 所需的时间为计算 Fib(n-1) 的时间和计算 Fib(n-2) 的时间的和。T(n<=1) = O(1),T(n)= T(n-1) + T(n-2) + O(1),通过使用递归树的结构描述可知算法复杂度为 O(2n)。
例2
int Fibonacci(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
else
{
int[] f = new int[n + 1];
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2];
}
returnf[n];
}
}
同样是斐波那契数列,我们使用数组 f 来存储计算结果,这样算法复杂度优化为 O(n)。
例3
int Fibonacci(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
else
{
int iter1 = 0;
int iter2 = 1;
int f = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
f = iter1 + iter2;
iter1 = iter2;
iter2 = f;
}
return f;
}
}
同样是斐波那契数列,由于实际只有前两个计算结果有用,我们可以使用中间变量来存储,这样就不用创建数组以节省空间。同样算法复杂度优化为 O(n)。
例4
通过使用矩阵乘方的算法来优化斐波那契数列算法。
static intFibonacci(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
int[,] f = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
Power(f, n - 1);
return f[0, 0];
}
static voidPower(int[,] f, int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return;
int[,] m = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
Power(f, n / 2);
Multiply(f, f);
if (n % 2 != 0)
Multiply(f, m);
}
static voidMultiply(int[,] f, int[,] m)
{
int x = f[0, 0] * m[0, 0] + f[0, 1] *m[1, 0];
int y = f[0, 0] * m[0, 1] + f[0, 1] *m[1, 1];
int z = f[1, 0] * m[0, 0] + f[1, 1] * m[1,0];
int w = f[1, 0] * m[0, 1] + f[1, 1] *m[1, 1];
f[0, 0] = x;
f[0, 1] = y;
f[1, 0] = z;
f[1, 1] = w;
}
优化之后算法复杂度为O(log2n)。
排序算法
1、快速排序
#include<cstdio>
inline void Rd(int&res){
res=0;char c;
while(c=getchar(),c<48);
dores=(res<<3)+(res<<1)+(c^48);
while(c=getchar(),c>47);
}
int res[100005];
void qsort(int L,intR){
if(L>=R)return;
int key=res[L],low=L,high=R;
while(low<high){
while(low<high&&key<=res[high])--high;
if(low<high)res[low++]=res[high];
while(low<high&&key>=res[low])++low;
if(low<high)res[high--]=res[low];
}
res[low]=key;
qsort(L,low-1),qsort(low+1,R);
}
int main(){
int n;Rd(n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)Rd(res[i]);
qsort(1,n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
printf("%d%c",res[i],i==n?'\n':' ');
}
2、归并排序
#include<cstdio>
inline void Rd(int&res){
res=0;char c;short f=1;
while(c=getchar(),c<48&&c!='-');
do if(c=='-')f=-1;
elseres=(res<<3)+(res<<1)+(c^48);
while(c=getchar(),c>47);
res*=f;
}
const int M=1000005;
int a[M],b[M];
void Merge(int L,intR){
if(L==R)return;
int mid=L+R>>1;
Merge(L,mid);Merge(mid+1,R);
int low=L,high=mid+1,c=L;
while(low<=mid&&high<=R)//[L,low)
if(a[low]<=a[high])b[c++]=a[low++];
else b[c++]=a[high++];
while(low<=mid)b[c++]=a[low++];
while(high<=R)b[c++]=a[high++];
for(int i=L;i<=R;i++)a[i]=b[i];
}
int main(){
int n;Rd(n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)Rd(a[i]);
Merge(1,n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
printf("%d%c",a[i],i==n?'\n':' ');
}
3、堆排序
#include<cstdio>
inline void Rd(int&res){
res=0;char c;
while(c=getchar(),c<48);
dores=(res<<3)+(res<<1)+(c^48);
while(c=getchar(),c>47);
}
struct Heap{
static const int M=100005;
int heap[M],sz;
Heap(){sz=0;}
inline void swap(int *a,int *b){
if(a==b)return;
int t=*a;*a=*b;*b=t;
}
int top(){return heap[1];}
void push(int val){
heap[++sz]=val;
int pos=sz;
while(pos>>1){
int nxt=pos>>1;
if(heap[nxt]>heap[pos])swap(&heap[nxt],&heap[pos]);
else break;
pos=nxt;
}
}
void pop(){
int pos=1;
heap[pos]=heap[sz--];
while((pos<<1)<=sz){
int nxt=pos<<1;
if(nxt+1<=sz&&heap[nxt+1]<heap[nxt])++nxt;
if(heap[nxt]<heap[pos])swap(&heap[pos],&heap[nxt]);
else break;
pos=nxt;
}
}
}q;
int main(){
int n;Rd(n);
for(int i=1,x;i<=n;++i)Rd(x),q.push(x);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
printf("%d",q.top());
putchar(i==n?'\n':' ');
q.pop();
}
}
4、基数排序
#include<cstdio>
inline void Rd(int&res){
res=0;char c;
while(c=getchar(),c<48);
dores=(res<<3)+(res<<1)+(c^48);
while(c=getchar(),c>47);
}
static const intM=100005,S=10;
inta[M],s[S][M],sz[S];
int main(){
int n;Rd(n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)Rd(a[i]);
for(int base=1,i=1;i<S;i++,base*=10){
for(int j=0;j<S;j++)sz[j]=0;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
int step=a[j]/base%10;
s[step][++sz[step]]=a[j];
}
int tot=0;
for(int j=0;j<S;j++)
for(int k=1;k<=sz[j];k++)
a[++tot]=s[j][k];
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
printf("%d%c",a[i],i==n?'\n':' ');
}


 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫